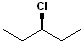
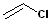
Haloalkane
(3-Chloropentane)
(Chloroethylene or vinyl chloride)
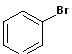
(Bromobenzene)
Haloalkanes (Alkyl Halides)
(The classes of compounds, in which a carbon atom is connected to a halogen)
Structure & Types
Compounds, which contain a halogen (F, Cl, Br or I) covalently bonded to an sp3 hybridized carbon are called- haloalkanes and given a general formula of R-X. If the carbon is sp2 hydridized, then the compound is called a haloalkenes (vinyl halide); finally, if the carbon is part of an aromatic ring, then the compound is a haloarene (aryl halide).
|
|
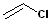 |
 |
|
Haloalkane (3-Chloropentane) |
Haloalkene (Chloroethylene or vinyl chloride) |
Haloarene (Bromobenzene) |
Basic IUPAC nomenclature-Haloalkanes: (See the home page for parent root names, prefixes & suffixes.)
1. Number the parent chain to give the substituent encountered first the lowest number, whether it is halogen or an alkyl group.
2. Indicate halogen substituents by the prefixes fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, and iodo- and list them in alphabetical order with other substituents.
3. Locate each halogen on the parent chain by giving it a number preceding the name of the halogen.
Examples:
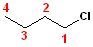 The
parent chain in this example is butane; numbering
the carbons, such that the chlorine will be on
carbon #1 will result in the name: 1-Chlorobutane.
The
parent chain in this example is butane; numbering
the carbons, such that the chlorine will be on
carbon #1 will result in the name: 1-Chlorobutane.
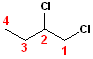 In
this example, the parent chain is still butane;
now, numbering the carbons, such that the chlorine atoms are on carbons #1 & #2.
Since there are two chlorines, the term dichloro-
is used. However, to specify the exact position of the two chlorine atoms, the
numbers are used: 1,2-Dichloro- is combined with
butane to become the full, IUPAC name:
1,2-Dichlorobutane.
In
this example, the parent chain is still butane;
now, numbering the carbons, such that the chlorine atoms are on carbons #1 & #2.
Since there are two chlorines, the term dichloro-
is used. However, to specify the exact position of the two chlorine atoms, the
numbers are used: 1,2-Dichloro- is combined with
butane to become the full, IUPAC name:
1,2-Dichlorobutane.
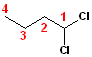 When
the chlorines are on the same carbon, they are still given the lowest number,
and the number is used twice: 1,1-Dichloro. When
added to the parent chain, butane, the name
becomes: 1,1-Dichlorobutane.
When
the chlorines are on the same carbon, they are still given the lowest number,
and the number is used twice: 1,1-Dichloro. When
added to the parent chain, butane, the name
becomes: 1,1-Dichlorobutane.
4. In haloalkenes, number the parent chain to give carbon atoms of the double bond the lower set of numbers.
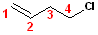 This
parent compound is a butene- the double bond is
given the preference (priority) in the numbering, so it is a
1-Butene. With the carbon framework in place &
numbered, the chlorine is on the #4 position and
the name becomes: 4-Chloro-1-butene. Note, that it
is necessary to specify where the double bond is placed as well as the chlorine
atom.
This
parent compound is a butene- the double bond is
given the preference (priority) in the numbering, so it is a
1-Butene. With the carbon framework in place &
numbered, the chlorine is on the #4 position and
the name becomes: 4-Chloro-1-butene. Note, that it
is necessary to specify where the double bond is placed as well as the chlorine
atom.
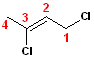 This
variation has the 2-butene parent name. Although
the butene can be numbered from the other direction (i.e. left to right), the
numbering is arranged such that the chlorines are positions 1 & 3 (as opposed to
2 & 4). Thus, the IUPAC name becomes: 2,3-Dichloro-2-butene.
This
variation has the 2-butene parent name. Although
the butene can be numbered from the other direction (i.e. left to right), the
numbering is arranged such that the chlorines are positions 1 & 3 (as opposed to
2 & 4). Thus, the IUPAC name becomes: 2,3-Dichloro-2-butene.
EXERCISE: Write the IUPAC name for each of the following structures.
| Structure | Name | Structure | Name | ||
| 1 | 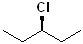 |
|
11 | 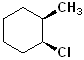 |
|
| 2 | 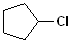 |
|
12 | 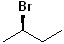 |
|
| 3 | 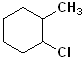 |
|
13 | 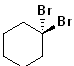 |
|
| 4 | 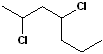 |
|
14 | 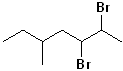 |
|
| 5 | 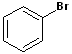 |
|
15 | 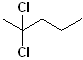 |
|
| 6 | 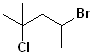 |
|
16 | 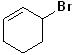 |
|
| 7 | 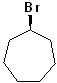 |
|
17 | 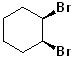 |
|
| 8 | 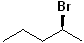 |
|
18 | 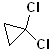 |
|
| 9 | 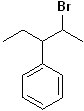 |
|
19 | 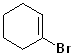 |
|
| 10 | 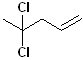 |
|
20 | 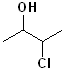 |
|
END OF SECTION
email questions & comments to: Dr. JA Colapret